Hebrew alphabet
| Hebrew alphabet | |
|---|---|
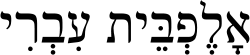 |
|
| Type | Abjad |
| Spoken languages | Hebrew, Yiddish, Ladino, and Judeo-Arabic (see Jewish languages) |
| Time period | 3rd century BCE to present |
| Parent systems |
Egyptian hieroglyphs
|
| Sister systems | Nabataean Syriac Palmyrenean Mandaic Brāhmī Pahlavi Sogdian |
| Unicode range | U+0590 to U+05FF, U+FB1D to U+FB40 |
| ISO 15924 | Hebr |
| Note: This page may contain IPA phonetic symbols. | |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
The Hebrew alphabet (Hebrew: אָלֶף-בֵּית עִבְרִי[a], Alephbet 'Ivri), known variously by scholars as the Jewish script, square script, block script, and because of its place of origin, the Assyrian script[1] (not to be confused with the Syriac alphabet) is used in the writing of the Hebrew language, as well as other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, and Judeo-Arabic. There have been two script forms in use. The original old Hebrew script is known as the paleo-Hebrew script (which has been largely preserved in the Samaritan script), while the present "square" form of the Hebrew alphabet is a stylized form of the Aramaic script. Various "styles" (in current terms, "fonts") of representation of the letters exist. There is also a cursive Hebrew script, which has also varied over time and place.
The Hebrew alphabet has 22 letters, five of which use different forms at the end of a word. Hebrew is written from right to left. Originally, the alphabet was an abjad consisting only of consonants. Like other abjads, such as the Arabic alphabet, means were later devised to indicate vowels by separate vowel points, known in Hebrew as niqqud. In rabbinic Hebrew, the letters א ה ו י are also used as matres lectionis to represent vowels. In modern usage of the alphabet, as in the case of Yiddish (except that ע replaces ה) and to some extent modern Israeli Hebrew, vowels may be indicated. Today, the trend is toward full spelling with these letters acting as true vowels.
Before the adoption of the present script, Hebrew was written by the ancient Israelites, both Jews and Samaritans, using the paleo-Hebrew alphabet. During the 3rd century BC, Jews began to use a stylized form of the Aramaic alphabet,[1] while the Samaritans continued to use a form of the paleo-Hebrew script, called the Samaritan script. The present "square script" Hebrew alphabet is a stylized version of the Aramaic alphabet which was adopted from that used by the Persian Empire (which in turn was adopted from the Arameans). After the fall of the Persian Empire, Jews used both scripts before settling on the Aramaic form. For a limited time thereafter, the use of the paleo-Hebrew script among Jews was retained only to write the Tetragrammaton, but soon that custom was also abandoned.
History

According to contemporary scholars, the original Hebrew script developed alongside others used in the region during the late second and first millennia BC. It is closely related to the Phoenician script, which itself probably gave rise to the use of alphabetic writing in Greece (Greek). A distinct Hebrew variant, called the paleo-Hebrew alphabet, emerged by the 10th century BC,[2] an example of which is represented in the Gezer calendar. It was commonly used in the ancient Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah.
Following the fall of the Kingdom of Judah in the 6th centuries BC, in the Babylonian exile, Jews adopted the Aramaic script, which was another offshoot of the same family of scripts, evolved into the Jewish, or "square" script, that is still in use today and known as the "Hebrew alphabet". The Samaritan script, used in writing Samaritan Hebrew, is descended directly from the paleo-Hebrew script.
The Hebrew alphabet was later adapted and used for writing languages of the Jewish diaspora - such as Karaim, Judæo-Arabic, Ladino, Yiddish, etc. The Hebrew alphabet came again into everyday use with the rebirth of the Hebrew language as a spoken language in the 18th and 19th centuries.
Description

General
In the traditional form, the Hebrew alphabet is an abjad consisting only of consonants, written from right to left. It has 22 letters, five of which use different forms at the end of a word. The Hebrew alphabet has only one case; there are no distinct capital or lowercase letters.
Vowels
In the traditional form, vowels are indicated by the weak consonants Aleph (א), He (ה), Vav (ו), or Yodh (י) serving as vowel letters, or matres lectionis: the letter is combined with a previous vowel and becomes silent, or by imitation of such cases in the spelling of other forms. Also, a system of vowel points to indicate vowels (diacritics), called niqqud, was developed. In modern forms of the alphabet, as in the case of Yiddish and to some extent modern Israeli Hebrew, vowels may be indicated. Today, the trend is toward full spelling with the weak letters acting as true vowels.
When used to write Yiddish, vowels are indicated, using certain letters, either with or without niqqud-diacritics (e.g., respectively: "אָ", "יִ" or "י", "ע", see Yiddish orthography), except for Hebrew words, which in Yiddish are written in their Hebrew spelling.
To preserve the proper vowel sounds, scholars developed several different sets of vocalisation and diacritical symbols called niqqud (ניקוד, literally "applying points"). One of these, the Tiberian system, eventually prevailed. Aaron ben Moses ben Asher, and his family for several generations, are credited for refining and maintaining the system. These points are normally used only for special purposes, such as Biblical books intended for study, in poetry or when teaching the language to children. The Tiberian system also includes a set of cantillation marks used to indicate how scriptural passages should be chanted, used in synagogue recitations of scripture (although these marks do not appear in the scrolls), called "trope". In everyday writing of modern Hebrew, niqqud are absent; however, patterns of how words are derived from Hebrew roots (called shorashim, or triliteral roots) allow Hebrew speakers to determine the vowel-structure of a given word from its consonants based on the word's context and part of speech.
The alphabet
Neither the old Hebrew script nor the modern Hebrew script have case, but five letters have special final forms,[c] called sofit (Heb. סופית, meaning in this case "final" or "ending") form, used only at the end of a word, somewhat as in the Arabic and Mandaic alphabets[b]. These are shown below the normal form, in the following table (letter names are Unicode standard; see variants of names and their pronunciation below). Hebrew is written from right to left.
| Alef | Bet | Gimel | Dalet | He | Vav | Zayin | Het | Tet | Yod | Kaf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| א | ב | ג | ד | ה | ו | ז | ח | ט | י | כ |
| ך | ||||||||||
| Lamed | Mem | Nun | Samekh | Ayin | Pe | Tsadi | Qof | Resh | Shin | Tav |
| ל | מ | נ | ס | ע | פ | צ | ק | ר | ש | ת |
| ם | ן | ף | ץ |
Note: The chart reads from right to left.
Pronunciation of letter names
See Hebrew phonology and Yiddish phonology for phonetic guides to the phonemic transcriptions.
| letter | Name of letter | Established pronunciation in English[3] |
standard Israeli pronunciation |
colloquial Israeli pronunciation (if differing) |
Yiddish / Ashkenazi pronunciation |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW[3] | Unicode | |||||
| א | Aleph | Alef | /ˈɑːlɛf/, /ˈɑːlɨf/ | /ˈalef/ | /ˈalɛf/ | |
| בּ | Beth | Bet | /bɛθ/, /beɪt/ | /bet/ | /bɛɪs/ | |
| ב | /vɛɪs/ | |||||
| ג | Gimel | Gimel | /ˈɡɪməl/ | /ˈɡimel/ | /ˈɡimːɛl/ | |
| ד | Daleth | Dalet | /ˈdɑːlɨθ/, /ˈdɑːlɛt/ | /ˈdalet/ | /ˈdaled/ | /ˈdalɛd/ |
| ה | He | He | /heɪ/ | /he/ | /hej/ | /hɛɪ/ |
| ו | Waw | Vav | /vɑːv/ | /vav/ | /vɔv/ | |
| ז | Zayin | Zayin | /ˈzaɪ.ɨn/ | /ˈzajin/ | /ˈza.in/ | /ˈzajin/ |
| ח | Heth | Het | /hɛθ/, /xeɪt/ | /ħet/ | /χet/ | / χɛs/ |
| ט | Teth | Tet | /tɛθ/, /teɪt/ | /tet/ | /tɛs/ | |
| י | Yod | Yod | /jɔːd/ | /jod/ | /jud/ | /jud/ |
| כּ | Kaph | Kaf | /kɑːf/ | /kaf/ | /kɔf/ | |
| כ | /χɔf/ | |||||
| ך | Final Kaf | /kaf sofit/ | /laŋɡɛ χɔf/ | |||
| ל | Lamed | Lamed | /ˈlɑːmɛd/ | /ˈlamed/ | /ˈlamɛd/ | |
| מ | Mem | Mem | /mɛm/ | /mem/ | /mɛm/ | |
| ם | Final Mem | /mem sofit/ | /ʃlɔs mɛm/ | |||
| נ | Nun | Nun | /nuːn/ | /nun/ | /nun/ | |
| ן | Final Nun | /nun sofit/ | /laŋgɛ nun/ | |||
| ס | Samekh | Samekh | /ˈsɑːmɛk/ | /ˈsameχ/ | /ˈsamɛχ/ | |
| ע | Ayin | Ayin | /ˈaɪ.ɨn/ | /ˈʕajin/ | /ˈa.in/ | /ˈajin/ |
| פּ | Pe | Pe | /peɪ/ | /pe/ | /pej/ | /pɛɪ/ |
| פ | /fɛɪ/ | |||||
| ף | Final Pe | /pe sofit/ | /pej sofit/ | /laŋɡɛ fɛɪ/ | ||
| צ | Sadhe | Tsadi | /ˈsɑːdə/, /ˈsɑːdi/ | /ˈtsadi/ | /ˈtsadik/ | /ˈtsɔdi/, /ˈtsɔdik/, /ˈtsadɛk/ |
| ץ | Final Tsadi | /ˈtsadi sofit/ | /ˈtsadik sofit/ | /laŋɡɛ ˈtsadɛk/ | ||
| ק | Qoph | Qof | /kɔːf/ | /kof/ | /kuf/ | /kuf/ |
| ר | Resh | Resh | /rɛʃ/, /reɪʃ/ | /reʃ/ | /rejʃ/ | /rɛɪʃ/ |
| ש | Shin | Shin | /ʃiːn/, /ʃɪn/ | /ʃin/ | /ʃin, sin/ | |
| תּ | Tav | Tav | /tɑːf/, /tɔːv/ | /tav/ | /taf/ | /tɔv/, /tɔf/ |
| ת | /sɔv/, /sɔf/ | |||||
Orthographic variants
The following table displays orthographic variants of each letter. For the five letters that have a different final form used at the end of words, the final forms are displayed beneath the regular form.
The three lettering variants currently in use are block, cursive and Rashi. Block and Rashi are used in books. Block lettering dominates, with Rashi lettering typically used for certain editorial inserts (as in the glosses of Isserles to the Shulchan Aruch) or biblical commentaries (as in the commentary of Rashi) in various standard literary works. Cursive is used almost exclusively when handwriting, unless block lettering is desired for stylistic purposes (as in signage).
For additional ancestral scripts, see Ancestral scripts and script variants.
| Letter name (Unicode) |
Variants | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modern Hebrew | Ancestral | |||||||
| Serif | Sans- serif |
Mono- spaced |
Cursive | Rashi | Phoenician | Paleo-Hebrew | Aramaic | |
| Alef | א | א | א | |||||
| Bet | ב | ב | ב | |||||
| Gimel | ג | ג | ג | |||||
| Dalet | ד | ד | ד | |||||
| He | ה | ה | ה | |||||
| Vav | ו | ו | ו | |||||
| Zayin | ז | ז | ז | |||||
| Het | ח | ח | ח | |||||
| Tet | ט | ט | ט | |||||
| Yod | י | י | י | |||||
| Kaf | כ | כ | כ | |||||
| Final Kaf | ך | ך | ך | |||||
| Lamed | ל | ל | ל | |||||
| Mem | מ | מ | מ | |||||
| Final Mem | ם | ם | ם | |||||
| Nun | נ | נ | נ | |||||
| Final Nun | ן | ן | ן | |||||
| Samekh | ס | ס | ס | |||||
| Ayin | ע | ע | ע | |||||
| Pe | פ | פ | פ | |||||
| Final Pe | ף | ף | ף | |||||
| Tsadi | צ | צ | צ | |||||
| Final Tsadi | ץ | ץ | ץ | |||||
| Qof | ק | ק | ק | |||||
| Resh | ר | ר | ר | |||||
| Shin | ש | ש | ש | |||||
| Tav | ת | ת | ת | |||||
Yiddish symbols
| Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|
| װ ױ ײ ײַ | These are intended for Yiddish. They are not used in Hebrew[d]. See: Yiddish orthography. |
| בֿ | The rafe (רפה) diacritic is no longer regularly used in Hebrew. In masoretic manuscripts and some other older texts the soft fricative consonants and sometimes matres lectionis are indicated by a small line on top of the letter. Its use has been largely discontinued in modern printed texts. It is still used to mark fricative consonants in the YIVO orthography of Yiddish. |
Numeric values of letters
Hebrew letters are also used to denote numbers, nowadays used only in specific contexts, e.g. denoting dates in the Hebrew calendar, denoting grades of school in Israel, other listings (e.g. שלב א׳, שלב ב׳ – "phase a, phase b"), commonly in Kabbalah (Jewish mysticism) in a practice known as gematria, and often in religious contexts.
| letter | numeric value | letter | numeric value | letter | numeric value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| א | 1 | י | 10 | ק | 100 | ||
| ב | 2 | כ | 20 | ר | 200 | ||
| ג | 3 | ל | 30 | ש | 300 | ||
| ד | 4 | מ | 40 | ת | 400 | ||
| ה | 5 | נ | 50 | ך | 500 | ||
| ו | 6 | ס | 60 | ם | 600 | ||
| ז | 7 | ע | 70 | ן | 700 | ||
| ח | 8 | פ | 80 | ף | 800 | ||
| ט | 9 | צ | 90 | ץ | 900 |
The numbers 500, 600, 700, 800 and 900 are often represented by the juxtapositions ק״ת, ר״ת, ש״ת, ת״ת, and ק״תת respectively. Adding a geresh ("׳") to a letter multiplies its value by one thousand, for example, the year 5769 is portrayed as ה׳תשס״ט, where ה represents 5000, and תשס״ט represents 769.
Transliterations and transcriptions of Hebrew letters
Main articles: Romanization of Hebrew, Hebrew phonology
The following table lists transliterations and transcriptions of Hebrew letters used in Modern Hebrew. For Hebrew vowel diacritics, see niqqud; for the phonology of Biblical Hebrew, see Biblical Hebrew; for the Yiddish language, see Yiddish orthography and Yiddish phonology.
Clarifications:
- For some letters, the Academy of the Hebrew Language offers a precise transliteration which differs from the regular standard it has set. When omitted, no such precise alternative exists and the regular standard applies.
- The IPA phonemic transcription is specified whenever it uses a different symbol than the one used for the regular standard Israeli transliteration.
- The IPA phonetic transcription is specified whenever it differs from IPA phonemic transcription.
Note: SBL's transliteration system, recommended in its Handbook of Style[4], differs slightly from the 2006 precise transliteration system of the Academy of the Hebrew Language; for "ו" SBL uses "v" (≠ AHL "w"), for "צ" SBL uses "ṣ" (≠ AHL "ẓ"), and for בג״ד כפ״ת with no dagesh, SBL uses the same symbols as for with dagesh (i.e. "b", "g", "d", "k", "f", "t").
| Click "show" to view extended table including examples. | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebrew letter | example | Translation | Standard Israeli transliteration – regular[5] |
example | standard Israeli transliteration – precise[5] |
example | IPA phonemic transcription |
example | IPA phonetic transcription |
example | ||||
| א
consonantal, in
initial word positions |
אִם | if | none[A1] | im | [ʔ] | [ʔim] | ||||||||
| א
consonantal, in
non initial word positions |
שָׁאַל | asked | ' | sha'ál | ʾ | shaʾál | /ʔ/ | /ʃaˈʔal/ | ||||||
| א
silent
|
רִאשׁוֹן | first | none[A2] | rishón | ||||||||||
| בּ | בֵּן | son | b | ben | ||||||||||
| ב | טוֹב | good | v | tov | ||||||||||
| גּ | גַּג | roof | g | gag | g | gaḡ | ||||||||
| ג | ḡ | |||||||||||||
| ג׳ | ג׳וּק | roach | ǧ[B1][6] | ǧuk | /d͡ʒ/ | /d͡ʒuk/ | ||||||||
| דּ | דּוּד | boiler | d | dud | d | duḏ | ||||||||
| ד | ḏ | |||||||||||||
| ה
consonantal
|
הֵד | echo | h | hed | ||||||||||
| ה
silent
|
פֹּה | here | none[A3] | po | ||||||||||
| ו
consonantal
|
וָו | hook | v | vav | w | waw | ||||||||
| וּ | הוּא | he | u | hu | ||||||||||
| וֹ | לוֹ | to him | o | lo | [o̞] or [ɔ̝] | [lo̞, lɔ̝] | ||||||||
| ז | זֶה | this | z | ze | ||||||||||
| ז׳ | זָ׳רְגוֹן | jargon | ž[B2][6] | žargón | /ʒ/ | /ʒarˈɡon/ | ||||||||
| ח | חַם | hot | ẖ [C1] | ẖam | ḥ | ḥam | /x/ or /χ/ | /xam/ | [χ] | [χam] | ||||
| dialectical [ħ] |
[ħam] | |||||||||||||
| ט | קָט | tiny | t | kat | ṭ | kaṭ | ||||||||
| י
consonantal
|
יָם | sea | y | yam | /j/ | /jam/ | ||||||||
| י
part of hirik male
(/i/ vowel) |
בִּי | in me | i | bi | ||||||||||
| י
part of tsere male
(/e/ vowel or /ei/ diphthong) |
מֵידָע | information | e | medá | é | médá | /e/ or /ej/ | /meˈda/ or /mejˈda/ | ||||||
| כּ, ךּ[7] | כֹּה | so | k | ko | ||||||||||
| כ, ך | סְכָךְ | branch-roofing | kh [C2] | skhakh | ḵ | sḵaḵ | /x/ or /χ/ | /sxax/ | [χ] | [sχaχ] | ||||
| ל | לִי | to me | l | li | ||||||||||
| מ, ם | מוּם | defect | m | mum | ||||||||||
| נ, ן | נִין | great-grandson | n | nin | ||||||||||
| ס | סוֹף | end | s | sof | ||||||||||
| ע
in initial or final
word positions |
עַדְלֹאיָדַע | Purim-parade | none[A4] | adloyáda | ʿ | ʿadloyádaʿ | only in initial word position [ʔ] |
[ˌʔadlo̞ˈjada] | ||||||
| dialectical /ʕ/ |
/ˌʕadloˈjadaʕ/ | |||||||||||||
| ע
in medial
word positions |
מוֹעִיל | useful | ' | mo'íl | ʿ | moʿíl | /ʔ/ | /moˈʔil/ | ||||||
| dialectical /ʕ/ |
/moˈʕil/ | |||||||||||||
| פּ[D] | טִיפּ | tip | p | tip | ||||||||||
| פ, ף | פִסְפֵס | missed | f | fisfés | ||||||||||
| צ, ץ | צִיץ | bud | ts | tsits | ẓ | ẓiẓ | /t͡s/ | /t͡sit͡s/ | ||||||
| צ׳, ץ׳ | ריצ׳רץ׳ | zip | č[B3][6] | ríčrač | /t͡ʃ/ | /ˈrit͡ʃrat͡ʃ/ | ||||||||
| ק | קוֹל | sound | k | kol | q | qol | ||||||||
| ר | עִיר | city | r | ir | [ʀ] or [ʁ] | [iʀ] or [iʁ] | ||||||||
| dialectical [r] or [ɾ] |
[ir] or [iɾ] | |||||||||||||
| שׁ | שָׁם | there | sh | sham | š | šam | /ʃ/ | /ʃam/ | ||||||
| שׂ | שָׂם | put | s | sam | ś | śam | ||||||||
| תּ | תּוּת | strawberry | t | tut | t | tuṯ | ||||||||
| ת | ṯ | |||||||||||||
| Hebrew letter | Standard Israeli transliteration – regular[5] |
standard Israeli transliteration – precise[5] |
IPA phonemic transcription |
IPA phonetic transcription |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| א
consonantal, in
initial word positions |
none[A1] | [ʔ] | ||||||
| א
consonantal, in
non initial word positions |
' | ʾ | /ʔ/ | |||||
| א
silent
|
none[A2] | |||||||
| בּ | b | |||||||
| ב | v | |||||||
| גּ | g | g | ||||||
| ג | ḡ | |||||||
| ג׳ | ǧ[B1][6] | /d͡ʒ/ | ||||||
| דּ | d | d | ||||||
| ד | ḏ | |||||||
| ה
consonantal
|
h | |||||||
| ה
silent
|
none[A3] | |||||||
| ו
consonantal
|
v | w | ||||||
| וּ | u | |||||||
| וֹ | o | [o̞] or [ɔ̝] | ||||||
| ז | z | |||||||
| ז׳ | ž[B2][6] | /ʒ/ | ||||||
| ח | ẖ[C1] | ḥ | /x/ or /χ/ | [χ] | ||||
| dialectical [ħ] |
||||||||
| ט | t | ṭ | ||||||
| י
consonantal
|
y | /j/ | ||||||
| י
part of hirik male
(/i/ vowel) |
i | |||||||
| י
part of tsere male
(/e/ vowel or /ei/ diphthong) |
e | é | /e/ or /ej/ | |||||
| כּ, ךּ[7] | k | |||||||
| כ, ך | kh[C2] | ḵ | /x/ or /χ/ | [χ] | ||||
| ל | l | |||||||
| מ, ם | m | |||||||
| נ, ן | n | |||||||
| ס | s | |||||||
| ע
in initial or final
word positions |
none[A4] | ʿ | only in initial word position [ʔ] |
|||||
| dialectical /ʕ/ |
||||||||
| ע
in medial
word positions |
' | ʿ | /ʔ/ | |||||
| dialectical /ʕ/ |
||||||||
| פּ[D] | p | |||||||
| פ, ף | f | |||||||
| צ, ץ | ts | ẓ | /t͡s/ | |||||
| צ׳, ץ׳ | č[B3][6] | /t͡ʃ/ | ||||||
| ק | k | q | ||||||
| ר | r | [ʀ] or [ʁ] | ||||||
| dialectical [r] or [ɾ] |
||||||||
| שׁ | sh | š | /ʃ/ | |||||
| שׂ | s | ś | ||||||
| תּ | t | t | ||||||
| ת | ṯ |
- Notes
A1^ 2^ 3^ 4^ In transliterations of modern Israeli Hebrew, initial and final ע (in regular transliteration), silent or initial א, and silent ה are not transliterated. To the eye of readers orientating themselves on Latin (or similar) alphabets, these letters might seem to be transliterated as vowel letters; however, these are in fact transliterations of the vowel diacritics – niqqud (or are representations of the spoken vowels). E.g., in אִם ("if", [ʔim]), אֵם ("mother", [ʔe̞m]) and אֹם ("nut", [ʔo̞m]), the letter א always represents the same consonant: [ʔ] (glottal stop), whereas the vowels /i/, /e/ and /o/ respectively represent the spoken vowel, whether it is orthographically denoted by diacritics or not. Since the Academy of the Hebrew Language ascertains that א in initial position is not transliterated, the symbol for the glottal stop ʾ is omitted from the transliteration, and only the subsequent vowels are transliterated (whether or not their corresponding vowel diacritics appeared in the text being transliterated), resulting in "im", "em" and "om", respectively.
B1^ 2^ 3^ The diacritic geresh – "׳" – is used with some other letters as well (ד׳, ח׳, ט׳, ע׳, ר׳, ת׳, see geresh), but only to transliterate from other languages to Hebrew – never to spell Hebrew words; therefore they were not included in this table (correctly translating a Hebrew text with these letters would require using the spelling in the language from which the transliteration to Hebrew was originally made). The non-standard "ו׳" and "וו" [e1] are sometimes used to represent /w/, which like /d͡ʒ/, /ʒ/ and /t͡ʃ/ appears in Hebrew slang and loanwords; see Hebrew Vav for the orthographic variants of vav.
C1^ 2^ The Sound /χ/ (as "ch" in loch) is often transcribed "ch", inconsistently with the guidelines specified by the Academy of the Hebrew Language: חם /χam/ → "cham"; סכך /sχaχ/ → "schach".
D^ Although the Bible does include a single occurrence of a final pe with a dagesh (Book of Proverbs 30, 6: "אַל-תּוֹסְףְּ עַל-דְּבָרָיו: פֶּן-יוֹכִיחַ בְּךָ וְנִכְזָבְתָּ."), in modern Hebrew /p/ is always represented by pe in its regular, not final, form "פ", even when in final word position, which occurs with loanwords (e.g. שׁוֹפּ /ʃop/ "shop"), foreign names (e.g. פִילִיפּ /ˈfilip/ "Philip") and some slang (e.g. חָרַפּ /χaˈrap/ "slept deeply").
Pronunciation
The descriptions that follow are based on the pronunciation of modern standard Israeli Hebrew. For a concise summary, see the article International Phonetic Alphabet for Hebrew. For further information on regional and historical variations in pronunciation, see Hebrew phonology.
| Letters | א | בּ | ב | ג | גּ | ג׳ | ד | דּ | ד׳ | ה | ו | וּ | וֹ | וו , ו׳
(non-standard) |
ז | ז׳ | ח | ט | י |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPA | [ʔ], ∅ | [b] | [v] | [ɡ] | [d͡ʒ] | [d] | [ð] | [h~ʔ], ∅ | [v] | [u] | [o̞] | [w] | [z] | [ʒ] | [χ]~[ħ] | [t] | [j] | ||
| Letters | ִי | כּ ךּ | ך כ | ל | ם מ | ן נ | ס | ע | פּ | פ ף | ץ צ | ץ׳ צ׳ | ק | ר | שׁ | שׂ | תּ | ת | ת׳ |
| IPA | [i] | [k] | [χ] | [l] | [m] | [n] | [s] | [ʔ]~[ʕ], ∅ | [p] | [f] | [t͡s] | [tʃ] | [k] | [ʁ] | [ʃ] | [s] | [t] | [θ] | |
Shin and sin
Shin and sin are represented by the same letter, ש, but are two separate phonemes. They are not mutually allophonic. When vowel diacritics are used, the two phonemes are differentiated with a shin-dot or sin-dot; the shin-dot is above the upper-right side of the letter, and the sin-dot is above the upper-left side of the letter.
| Symbol | Name | Transliteration | IPA | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| שׂ (left dot) | sin | s | /s/ | sour |
| שׁ (right dot) | shin | sh | /ʃ/ | shop |
Historically, left-dot-sin, corresponds to Proto-Semitic *ś, which in biblical-Judaic-Hebrew corresponded to a voiceless alveolar lateral fricative /ɬ/, as is evident in Greek transliteration of Hebrew words such as Balsam (בֹּשֶׂם) (the ls - 'שׂ') as is evident in the Targum Onkelos. Rendering of proto-semitic *ś as /ɬ/, is still evident in the Soqotri language.
Dagesh
Historically, the consonants ב bet,beis, ג gimel, ד dalet, כ kaf,kof, פ pe,pey, and ת tav each had two sounds: one hard (plosive), and one soft (fricative), depending on the position of the letter and other factors. When vowel diacritics are used, the hard sounds are indicated by a central dot called dagesh (דגש), while the soft sounds lack a dagesh. In modern Hebrew, however, the dagesh only changes the pronunciation of ב bet, כ kaf, and פ pe. The differences are as follows:
| With dagesh | Without dagesh | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | Name | Transliteration | IPA | Example | Symbol | Name | Transliteration | IPA | Example |
| בּ | bet | b | /b/ | bun | ב | vet | v | /v/ | van |
| [7]כּ ךּ | kaph | k | /k/ | kangaroo | כ ך | khaph | kh/ch/k | /χ/ | loch |
| פּ | pe | p | /p/ | pass | פ ף | phe | ph/f | /f/ | find |
In other dialects (mainly liturgical) there are variations from this pattern.
- In some Sephardi and Mizrahi dialects, bet without dagesh is pronounced [b], like bet with dagesh
- In Syrian and Yemenite Hebrew, gimel without dagesh is pronounced [ɣ]
- In Yemenite Hebrew, and in the Iraqi pronunciation of the word "Adonai", dalet without dagesh is pronounced [ð] as in "these"
- In Ashkenazi Hebrew, tav without dagesh is pronounced [s] as in "silk"
- In Iraqi and Yemenite Hebrew, and formerly in some other dialects, tav without dagesh is pronounced [θ] is in "thick"
Identical pronunciation
In Israel's general population, many consonants have the same pronunciation. They are:
| Letters | Transliteration | Pronunciation (IPA) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| א Alef* |
ע Ayin* |
- | /Vowel Under Its Sound/ | ||
| ב Bet (without dagesh) |
ו Vav |
v | /v/ | ||
| ח Het |
כ Kaf (without dagesh) |
kh/ch/h | /χ/ | ||
| ט Tet |
ת Tav |
t | /t/ | ||
| כּ Kaf (with dagesh) |
ק Qof |
k | /k/ | ||
| ס Samekh |
שׂ Sin (with left dot) |
s | /s/ | ||
| צ Tsadi* |
תס Tav-Samekh* |
and | תשׂ Tav-Sin* |
ts/tz | /ts/ |
* Varyingly
Ancient Hebrew pronunciation
Some of the variations in sound mentioned above are due to a systematic feature of Ancient Hebrew. The six consonants /b ɡ d k p t/ were pronounced differently depending on their position. These letters were also called BeGeD KePHeT letters (pronounced /ˌbeɪɡɛdˈkɛfɛt/ in English). (The full details are very complex; this summary omits some points.) They were pronounced as stops b ɡ d k p t at the beginning of a syllable, or when doubled. They were pronounced as fricatives v ɣ ð x f θ when preceded by a vowel (commonly indicated with a macron, ḇ ḡ ḏ ḵ p̄ ṯ). The stop and double pronunciations were indicated by the dagesh. In Modern Hebrew the sounds ḏ and ḡ have reverted to [d] and [ɡ], respectively, and ṯ has become [t], so only the remaining three consonants /b k p/ show variation. ר "reish" may have also been a "doubled" letter, making the list BeGeD KePoReS. (Sefer Yetzirah, 4:1)
- ח chet and ע ayin represented pharyngeal fricatives, צ tsadi represented the emphatic consonant /sˤ/, ט tet represented the emphatic consonant /tˤ/, and ק qoph represented the uvular plosive /q/. All these are common Semitic consonants.
- שׂ sin (the /s/ variant of ש shin) was originally different from both שׁ shin and ס samekh, but had become /s/ the same as ס samekh by the time the vowel pointing was devised. Because of cognates with other Semitic languages, this phoneme is known to have originally been a lateral consonant, most likely the voiceless alveolar lateral fricative /ɬ/ (the sound of modern Welsh ll) or the voiceless alveolar lateral affricate /tɬ/ (like Náhuatl tl).
Vowels
Matres lectionis
א aleph, ה he, ו vav and י yod are letters that can sometimes indicate a vowel instead of a consonant (which would be, respectively, /ʔ/, /h/, /v/ and /j/). When they do, ו and י are considered to constitute part of the vowel designation in combination with a niqqud symbol – a vowel diacritic (whether or not the diacritic is marked), whereas א and ה are considered to be mute, their role being purely indicative of the non-marked vowel.
-
Letter Name
of letterConsonant
indicated
when letter
consonantalVowel
designationName of
vowel designationIndicated
Vowelא aleph /ʔ/ — — ê, ệ, ậ, â, ô ה he /h/ — — ê, ệ, ậ, â, ô ו vav /v/ וֹ ḥolám malé ô וּ shurúq û י yud /j/ ִי ḥiríq malé î ֵי tseré malé ê, ệ
Vowel points
Niqqud is the system of dots that help determine vowels and consonants. In Hebrew, all forms of niqqud are often omitted in writing, except for children's books, prayer books, poetry, foreign words, and words which would be ambiguous to pronounce. Israeli Hebrew has five vowel phonemes, /i e a o u/, but many more written symbols for them:
| Name | Symbol | Israeli Hebrew | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPA | Transliteration | English example |
||
| Hiriq | [i] | i | see | |
| Zeire | [ɛ] | e | men | |
| Segol | [ɛ], ([ɛi] with succeeding yod) |
e, (ei with succeeding yod) |
men | |
| Patach | [a] | a | car | |
| Kamatz | [a], <car>(or [ɔ]) | a, (or o)</car> | car | |
| Holam | סֹ | [ɔ] | o | cone |
| Shuruk | [u] | u | tube | |
| Kubutz | [u] | u | tube | |
Note 1: The symbol "O" represents whatever Hebrew letter is used.
Note 2: The pronunciation of zeire and sometimes segol - with or without the letter yod - is sometimes ei in Modern Hebrew. This is not correct in the normative pronunciation and not consistent in the spoken language.[8]
Note 3: The dagesh, mappiq, and shuruk have different functions, even though they look the same.
Note 4: The letter ו (vav) is used since it can only be represented by that letter.
Sh'va
By adding two vertical dots (called Sh'va) underneath the letter, the vowel is made very short.
| Name | Symbol | Israeli Hebrew | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPA | Transliteration | English example |
||
| Shva | [ɛ] or Ø | apostrophe, e, or nothing |
silent | |
| Reduced Segol | [ɛ] | e | men | |
| Reduced Patach | [a] | a | cup | |
| Reduced Kamatz | [ɔ] | o | cone | |
Comparison table
| Vowel comparison table | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vowel Length (phonetically not manifested in Israeli Hebrew) |
IPA | Transliteration | English example |
||
| Long | Short | Very Short | |||
| ָ | ַ | ֲ | [a] | a | spa |
| ֵ | ֶ | ֱ | [ɛ] | e | temp |
| וֹ | ָ | ֳ | [ɔ] | o | cone |
| וּ | ֻ | n/a | [u] | u | tube |
| ִי | ִ | [i] | i | ski | |
| Note I: | By adding two vertical dots (sh'va) ְ the vowel is made very short. |
||||
| Note II: | The short o and long a have the same niqqud. | ||||
| Note III: | The short o is usually promoted to a long o in Israeli writing for the sake of disambiguation |
||||
| Note IV: | The short u is usually promoted to a long u in Israeli writing for the sake of disambiguation |
||||
Gershayim
The symbol ״ is called a gershayim and is a punctuation mark used in the Hebrew language to denote acronyms. It is written before the last letter in the acronym. Gershayim is also the name of a note of cantillation in the reading of the Torah, printed above the accented letter.
Sounds represented with diacritic geresh
The sounds [t͡ʃ], [d͡ʒ], [ʒ], written "צ׳", "ג׳", "ז׳", and [w], non-standardly sometimes transliterated וו or ו׳[e3], are often found in slang and loanwords that are part of the everyday Hebrew colloquial vocabulary. The apostrophe-looking symbol after the Hebrew letter modifies the pronunciation of the letter and is called a geresh. (As mentioned above, while still done, using ו׳ to represent [w] is non-standard; standard spelling rules allow no usage of ו׳ whatsoever[e4]).
| Hebrew slang and loanwords | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Symbol | IPA | Transliteration | Example | ||
| Gimel with a geresh | ג׳ | [d͡ʒ] | ǧ[6] | ǧáḥnun | [ˈd͡ʒaχnun] | גָ׳חְנוּן |
| Zayin with a geresh | ז׳ | [ʒ] | ž[6] | koláž | [koˈlaʒ] | קוֹלָאז׳ |
| Tsadi with a geresh | צ׳ | [t͡ʃ] | č[6] | čupár (treat) | [t͡ʃuˈpar] | צ׳וּפָּר |
| Vav with a geresh or double Vav |
וו or ו׳(non standard)[e5] | [w] | w | awánta (boastful act) | [aˈwanta] | עָוָנְטָה |
The pronunciation of the following letters can also be modified with the geresh diacritic, the represented sounds are however foreign to Hebrew phonology, i.e., these symbols only represent sounds in foreign words or names when transliterated with the Hebrew alphabet, and never loanwords.
| Transliteration of non-native sounds | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Symbol | IPA | Arabic letter | Example | Comment | |
| Dalet with a geresh | ד׳ | [ð] | Ḏāl (ذ) Voiced th |
Dhu al-Hijjah (ذو الحجة) | ד׳ו אל-חיג׳ה | * Also used for English voiced th * Often a simple ד is written. |
| Tav with a geresh | ת׳ | [θ] | Ṯāʾ (ﺙ) Voiceless th |
Thurston | ת׳רסטון | |
| Ḥet with a geresh | ח׳ | [χ] | Ḫāʼ (خ) | Sheikh (شيخ) | שייח׳ | * Unlike the other sounds in this table, the sound [χ] represented by ח׳ is indeed a native sound in Hebrew; the geresh is however used only when transliteration must distinguish between [χ] and [ħ], in which case ח׳ transliterates the former and ח the latter, whereas in everyday usage ח without geresh is pronounced [ħ] only dialectically but [χ] commonly. |
| Resh with a geresh | ר׳ | [ʁ] | Ġayn (غ) | Ghajar | ר׳ג׳ר | Sometimes an Ayin with a geresh (ע׳) is used to transliterate غ – inconsistently with the guidelines specified by the Academy of the Hebrew Language |
A geresh is also used to denote initialisms and to denote a Hebrew numeral. Geresh also is the name of one of the notes of cantillation in the reading of the Torah, but its appearance and function is different.
In Jewish faith
The letters of the Hebrew alphabet have played varied roles in Jewish religious literature over the centuries, primarily in mystical texts. Some sources in classical rabbinical literature seem to acknowledge the historical provenence of the currently used Hebrew alphabet and deal with them as a mundane subject (the Jerusalem Talmud, for example, records that "the Israelites took for themselves square calligraphy", and that the letters "came with the Israelites from Ashur [Assyria]"[9]); others attribute mystical significance to the letters, connecting them with the process of creation or the redemption. In mystical conceptions, the alphabet is considered eternal, pre-existent to the Earth, and the letters themselves are seen as having holiness and power, sometimes to such an extent that several stories from the Talmud illustrate the idea that they cannot be destroyed.[10]
The idea of the letters' creative power finds its greatest vehicle in the Sefer Yezirah, or Book of Creation, a mystical text of uncertain origin which describes a story of creation highly divergent from that in the Book of Genesis, largely through exposition on the powers of the letters of the alphabet. The supposed creative powers of the letters are also referenced in the Talmud and Zohar.[11][12]
Another book, the thirteenth-century Kabbalistic text Sefer ha-Temunah, holds that a single letter of unknown pronunciation, held by some to be the four-pronged shin on one side of the teffilin box, is missing from the current alphabet. The world's flaws, the book teaches, are related to the absence of this letter, the eventual revelation of which will repair the universe.[13] Another example of messianic significance attached to the letters is the teaching of Rabbi Eliezer that the five letters of the alphabet with final forms hold the "secret of redemption".[13]
In addition, the letters occasionally feature in aggadic portions of non-mystical rabbinic literature. In such aggada the letters are often given anthropomorphic qualities and depicted as speaking to God. Commonly their shapes are used in parables to illustrate points of ethics or theology. An example from the Babylonian Talmud (a parable intended to discourage speculation about the universe before creation):
Why does the story of creation begin with bet?... In the same manner that the letter bet is closed on all sides and only open in front, similarly you are not permitted to inquire into what is before or what was behind, but only from the actual time of Creation.
Extensive instructions about the proper methods of forming the letters are found in Mishnat Soferim, within Mishna Berura of Yisrael Meir Kagan.
Unicode and HTML
The Unicode Hebrew block extends from U+0590 to U+05FF and from U+FB1D to U+FB40. It includes letters, ligatures, combining diacritical marks (niqqud and cantillation marks) and punctuation. The Numeric Character References is included for HTML. These can be used in many markup languages, and they are often used in Wiki to create the Hebrew glyphs compatible with the majority of web browsers.
See also
| Semitic alphabets |
|---|
| Phoenician (c.1050 – 200 BCE) |
|
Semitic abjads · Genealogy |
| Hebrew (400 BCE – present) |
|
History · Transliteration |
| Syriac (200 BCE – present) |
|
|
| Arabic (400 CE – present) |
|
History · Transliteration |
- Hebrew punctuation
- Significance of numbers of Judaism
- Mater lectionis
- History of the Hebrew language
- Syriac alphabet
- Niqqud
- Dagesh
- Gershayim
- Hebrew braille
- Cursive Hebrew
- Rashi script
- Ashuri alphabet
- Hebrew keyboard
- Romanization of Hebrew
- Hebrew phonology
- Inverted nun
- Koren Type
- Help:Hebrew
Notes
a^ "Aleph-bet" is commonly written in Israeli Hebrew without the maqaph (מקף, hyphen), אלפבית עברי, as opposed to with the hyphen, אלף־בית עברי.
b^ The Arabic letters have, in principle (as six of the primary letters can have only two variants), four forms, according to their place in the word. The same goes with the Mandaic ones, except for three of the 22 letters, which have only one form. For more information, see Arabic alphabet and Mandaic alphabet.
c^ In forms of Hebrew older than Modern Hebrew, כ״ף, בי״ת and פ״א can only be read b, k and p, respectively, at the beginning of a word, while they will have the sole value of v, kh and ph in a sofit (final) position, with few exceptions.[7] In medial positions, both pronunciations are possible. In Modern Hebrew this restriction is not absolute, e.g. פִיזִיקַאי /fiziˈkaj/ and never /piziˈkaj/ (= "physicist"), סְנוֹבּ /snob/ and never /snov/ (= "snob"). A dagesh may be inserted to unambiguously denote the plosive variant: בּ = /b/, כּ = /k/, פּ =/p/; similarly (though today very rare in Hebrew and common only in Yiddish) a rafé placed above the letter unambiguously denotes the fricative variant: בֿ = /v/, כֿ = /χ/ and פֿ = /f/.
d^ However, וו (two separate vavs), used in Ktiv male, is to be distinguished from the Yiddish ligature װ (also two vavs but together as one character).
e1^ e2^ e3^ e4^ e5^ The Academy of the Hebrew Language states that both [v] and [w] be indistinguishably represented in Hebrew using the letter Vav.[14] Sometimes the Vav is indeed doubled, however not to denote [w] as opposed to [v] but rather, when spelling without niqqud, to denote the phoneme /v/ at a non-initial and non-final position in the word, whereas a single Vav at a non-initial and non-final position in the word in spelling without niqqud denotes one of the phonemes /u/ or /o/. To pronounce foreign words and loanwords containing the sound [w], Hebrew readers must therefore rely on former knowledge and context, see also pronunciation of Hebrew Vav.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 A History of the Hebrew Language. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press. 1993. ISBN 0-521-55634-1.
- ↑ Ancient Scripts.com:Old Hebrew
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Merriam Webster's Collegiate Dictionary
- ↑ See online overview at Biblical Hebrew Resources
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Transliteration guidelines by the Academy of the Hebrew Language, November 2006
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 Transliteration guidelines preceding 2006-update, p. 2 Academy of the Hebrew Language
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 "ךּ" is rare but exists, e.g. last word in Deuteronomy 7 1 (דברים פרק ז׳ פסוק א׳) in the word "מִמֶּךָּ" – see תנ״ך מנוקד, דברים פרק ז׳
- ↑ Laufer, Asher (2008). Chapters in Phonetics and Phonetic Transcription. Jerusalem: Magnes. pp. 207–211. ISBN 0004503510837.
- ↑ Jerusalem Talmud, Tractate Sanhedrin 21b
- ↑ Babylonian Talmud, Tractate Pesach 87b, Avodah Zarah 18a
- ↑ Babylonian Talmud, Tractate Berachot 55c
- ↑ Zohar 1:3; 2:152
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 The Book of Letters. Woodstock, Vermont: Jewish Lights Publishing, Woodstock. 1990
- ↑ "Transliteration Rules" (PDF). http://hebrew-academy.huji.ac.il/PDF/taatiq2007.pdf. issued by the Academy of the Hebrew Language.
Bibliography
 Gesenius' Hebrew Grammar, §5 ff.
Gesenius' Hebrew Grammar, §5 ff.- Hoffman, Joel M. 2004. In the Beginning: A Short History of the Hebrew Language. New York: New York University Press.
- Saenz-Badillos, Angel. 1993. A History of the Hebrew Language. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
- Steinberg, David. History of the Hebrew Language.
- Mathers table
- Aleph-Beth Quick Study Chart. February 28, 2005. Qumran Bet Community. Retrieved January 5, 2006.
External links
- Hebrew alphabet lesson
- How to draw letters
- Official Unicode standards document for Hebrew
- Transliterate your English name into Hebrew Letters
Keyboards
- LiteType.com - Virtual & Interactive Hebrew Keyboard
- Mikledet.com - for typing Hebrew with an English keyboard (Hebrew keyboard|Hebrew layout)
- Hebrew Writing - Typing Hebrew and Nikud using extended English keyboard (Hebrew keyboard|Hebrew Writing layout)
- Prize Find: Oldest Hebrew Inscription Biblical Archaeology Review
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
